Last summer, residents on the island of Borneo were treated to a surprise light show as the core stage of a Chinese rocket fell out of orbit and lit up the night sky. Weighing 21.3 tons upon re-entry, the rocket broke apart into flaming human-made meteors. A local news report shows what appears to be a large fragment of the rocket in a field in West Kalimantan, an Indonesian province on Borneo.
Though there were no reported damages from the uncontrolled re-entry of the Chinese rocket, the incident raised eyebrows in the space community. Analysts had warned that the rocket stage was massive enough for fragments to have reached the earth’s surface in an area roughly 1,200 miles long and 44 miles wide.
The rocket, known as Long March 5B, is China’s largest and was part of the third mission since 2020 to deliver modules to China’s Tiangong space station that’s expected to be up and running by the end of the year. Two previous Long March 5B missions, in 2020 and 2021, led to similar uncontrolled re-entries over the Indian Ocean and Côte d’Ivoire. (These are 25 of the most dangerous things around Earth right now.)
The three Long March rocket core stages are among ten heaviest spacecraft to have crashed uncontrollably back to earth, each weighing 21 to 22 tons. Only four other human-made objects have crashed uncontrollably back to earth were heavier, including two Russian space stations, in 1979 and 1991, and the Space Shuttle Columbia, which exploded on re-entry in 2003, killing its seven-member crew.
Not all re-entries are uncontrolled. Following careful planning, the Russian space station Mir was deorbited into a controlled crash in the South Pacific Ocean east of New Zealand, giving residents of Fiji a spectacular light show. Space debris frequently falls back to earth, but most of it is small enough to burn up in the atmosphere. However, experts warn that the chance of space debris falling and injuring or killing people is not zero.
To identify the largest spacecraft or pieces of space debris to crash to earth in an uncontrolled manner, 24/7 Tempo examined online resources, including Space.com and a log of uncontrolled re-entries of orbital objects like booster rockets, satellites, and spacecraft by Jonathan McDowell, an astronomer at the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and publisher of “Jonathan’s Space Report,” a newsletter that tracks and describes space launches and satellites.
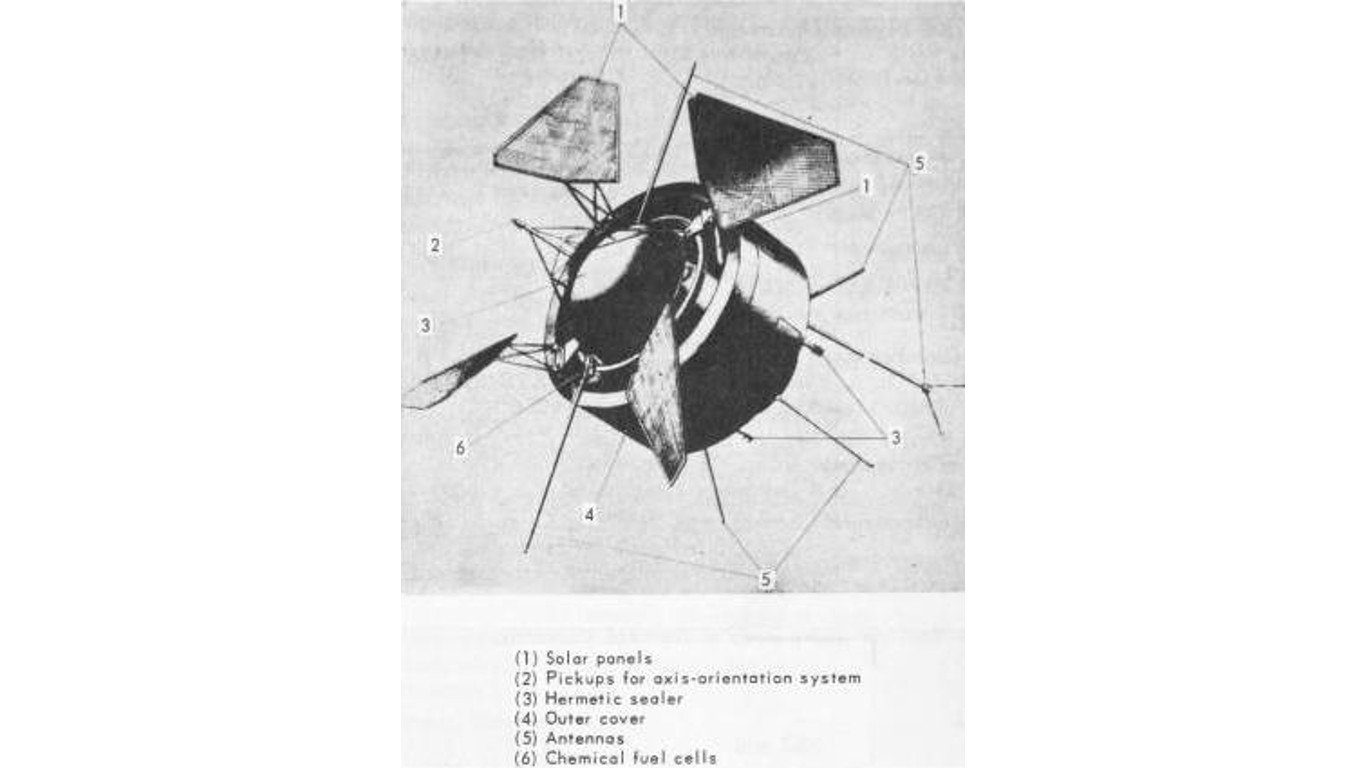
10. Proton-4
> Reentry Weight: 17 tons
> Re-entry location: Unknown
> Date of crash: July 24, 1969
Proton 4 was the heaviest of four Proton satellites launched by Russia from 1965 to 1968, all of which crashed back to earth at unknown locations. The Proton program launched research satellites and is considered to have played a key role in heralding a new era of Soviet space exploration.
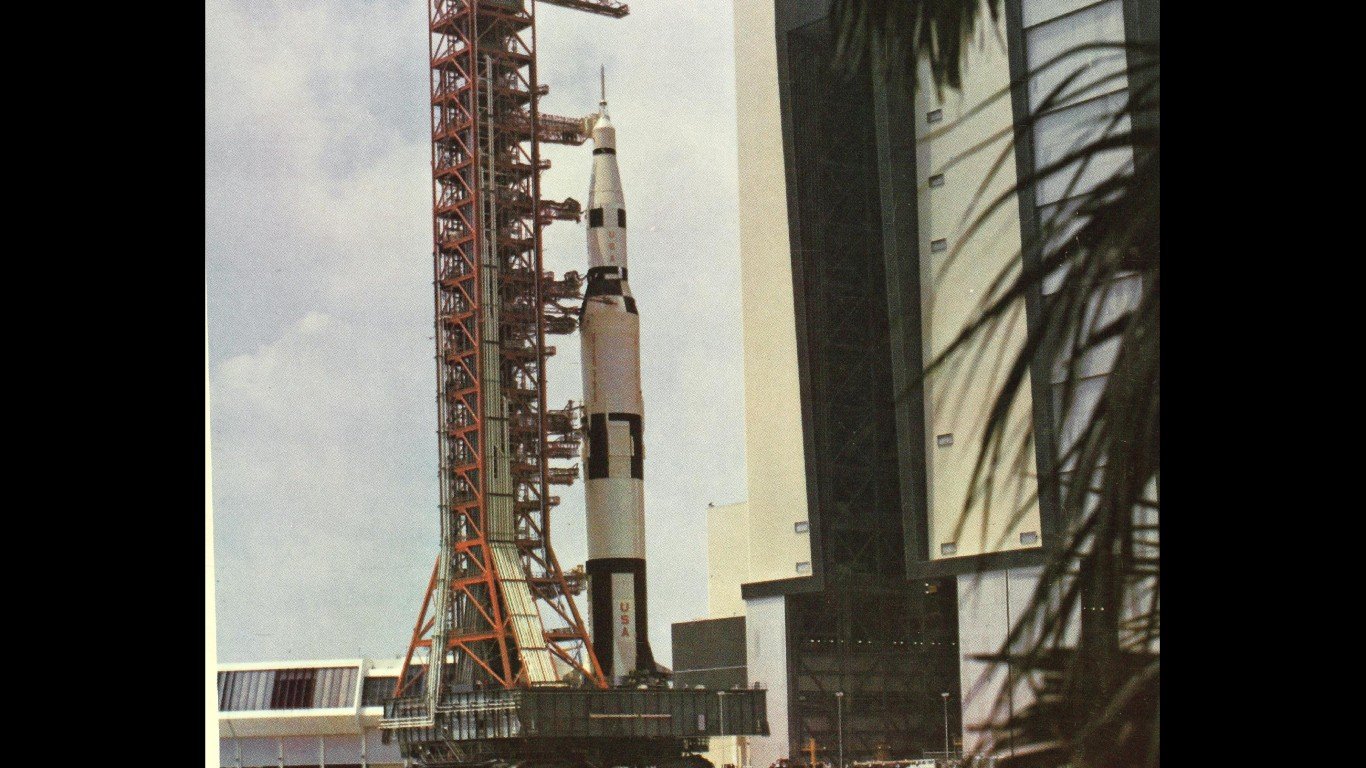
9. Saturn SA-5 rocket
> Reentry Weight: 17.2 tons
> Re-entry location: Brazil
> Date of crash: April 30, 1966
The Saturn SA-5 was part of the U.S. Apollo program, an orbital test rocket wielding a Jupiter nose cone containing measuring instruments instead of the Apollo command module that would later be used to send American astronauts into space. The Saturn SA-5 orbited for nearly 800 days before decaying into an uncontrolled re-entry.
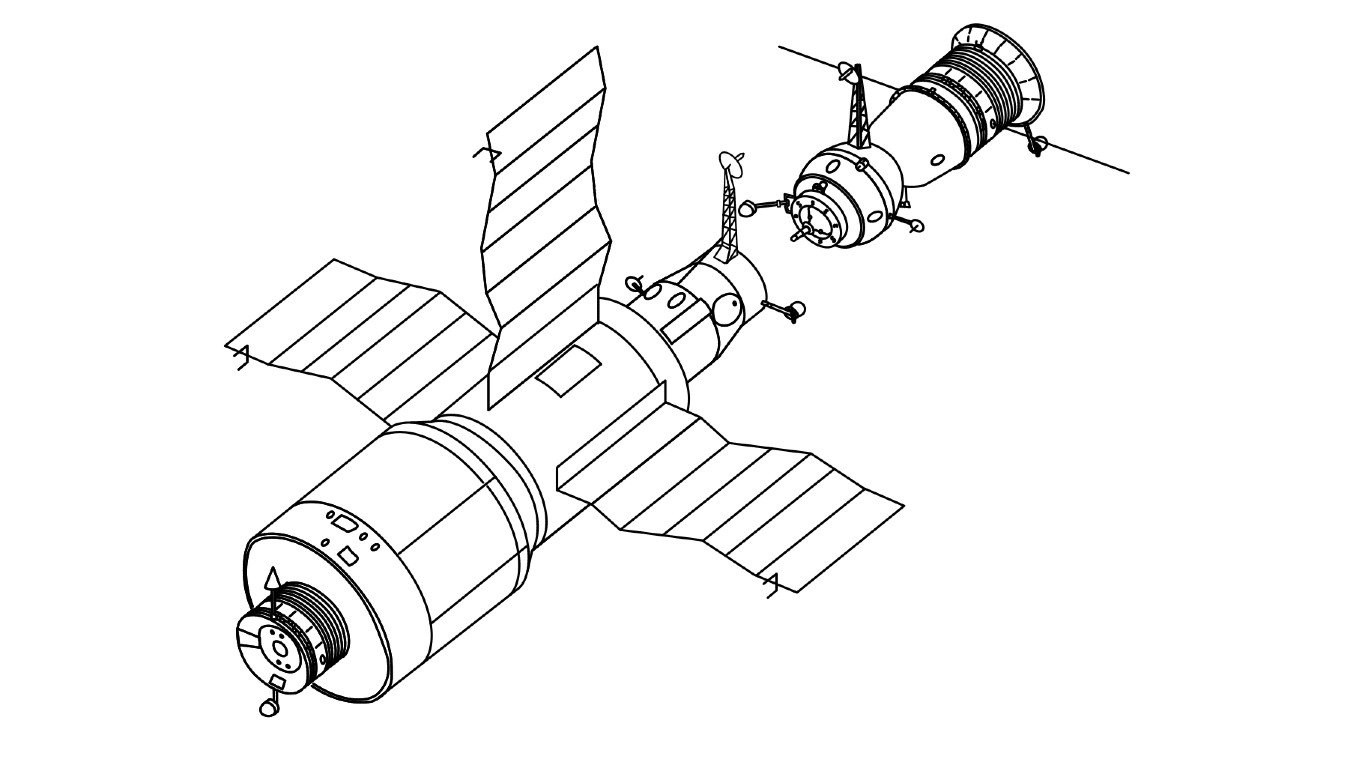
8. Kosmos-557
> Reentry Weight: 18.5 tons
> Re-entry location: Indian Ocean
> Date of crash: May 22, 1973
Part of the Russian Salyut space station program that put six crewed stations in orbit from 1971 to 1986, Kosmos 557 was later revealed to be a code name for a Salyut program station that failed to reach a stable orbit due to errors in the flight control system. Despite this failure, the Salyut program became another achievement for Russia’s space program, as it was the first to put a crewed space station in orbit.
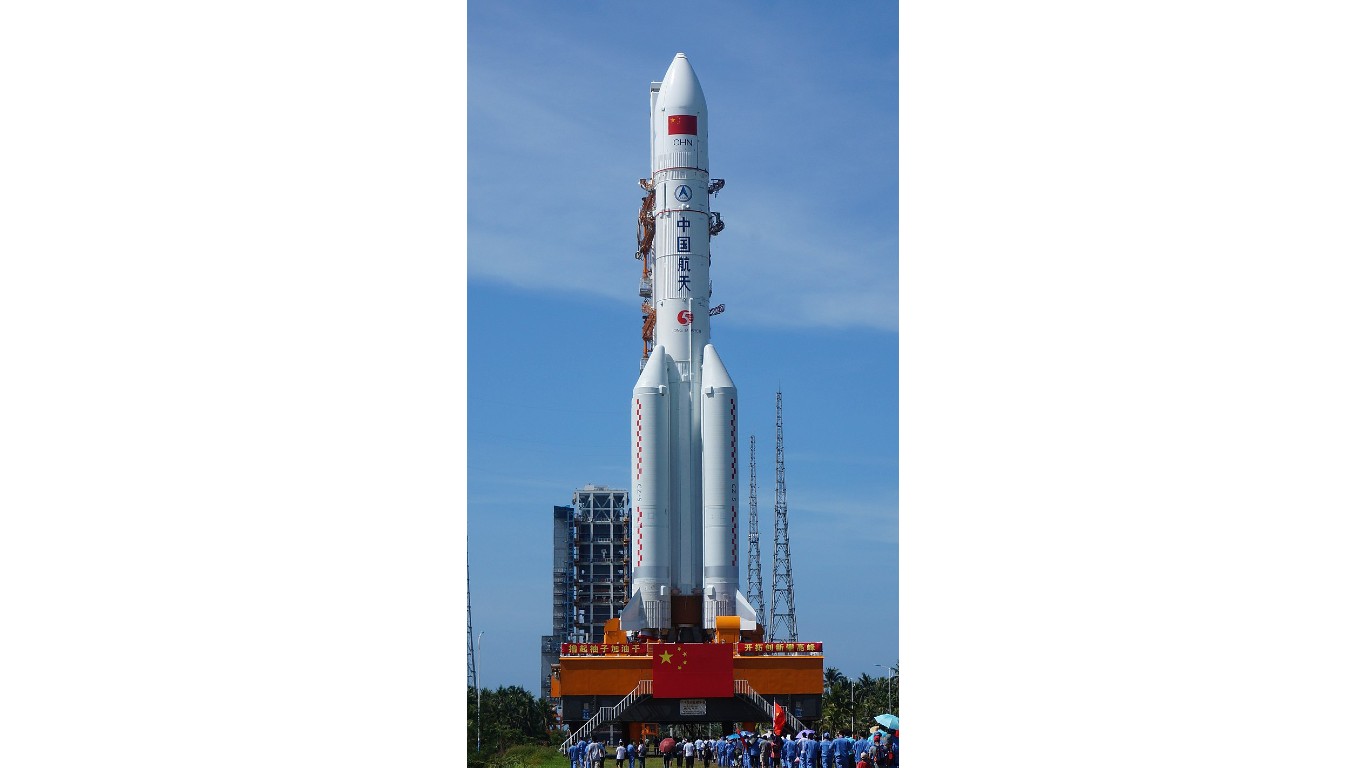
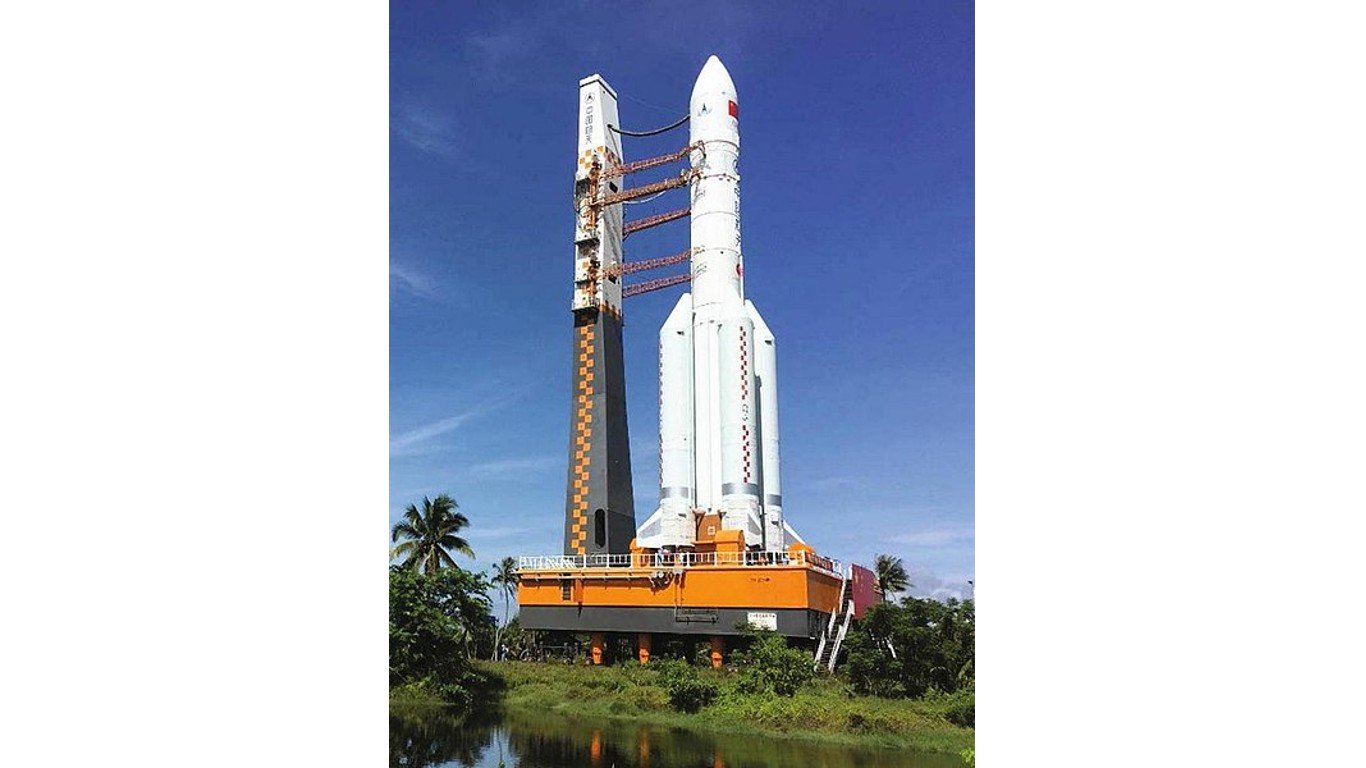
7. CZ-5B-Y3 (Long March 5B) core stage
> Reentry Weight: 21.3 tons
> Re-entry location: Sarawak, Malaysia
> Date of crash: July 30, 2022
CZ-5B-Y3 was the most recent of three uncontrolled reentries of massive Chinese Long March B core rocket stages that have plunged back to earth since 2020. In an indirect reference to China’s unwillingness to share data on the rocket’s descent trajectory, NASA Administrator Bill Nelson urged nations with space programs to “do their part to share this type of information in advance to allow reliable predictions of potential debris impact risk…to ensure the safety of people here on Earth.”
6. CZ-5B-Y2 (Long March 5B) core stage
> Reentry Weight: 21.3 tons
> Re-entry location: Indian Ocean, west of the Maldives
> Date of crash: May 9, 2021
CZ-5B-Y2 is the second of three massive Chinese Long March 5B rocket stages to have crashed uncontrollably to earth since 2020 after re-entering the atmosphere above the Arabian Peninsula. Long March 5B missions have been sending payloads to China’s Tiangong space station, which is expected to be online by the end of the year.
5. CZ-5B-Y1 (Long March 5B) core stage
> Reentry Weight: 21.6 tons
> Re-entry location: Côte d’Ivoire
> Date of crash: May 11, 2020
The CZ-5B-Y1 Long March 5B core rocket stage became the heaviest object to plunge to earth in an uncontrolled manner since the 39-ton Soviet Salyut 7 space station rained debris over Argentina in 1991. Fragments from the rocket stage fell onto at least two villages in the West African country of Ivory Coast, though no injuries were reported. All three Long March 5B rocket missions have involved uncontrolled reentries of massive rocket stages.
4. Salyut 7
> Reentry Weight: 39 tons
> Re-entry location: Argentina
> Date of crash: Feb. 7, 1991
After nine years in orbit, the Soviet space station Salyut 7 with an attached Kosmos 1686 unmanned spacecraft became at the time the largest spacecraft to plunge back to earth. Efforts by Soviet engineers to guide the de-crewed Salyut-7/Kosmos-1686 complex into the Atlantic Ocean in a controlled descent failed. The space station complexes broke up on its descent, showering debris near the Argentinean town of Capitán Bermúdez.
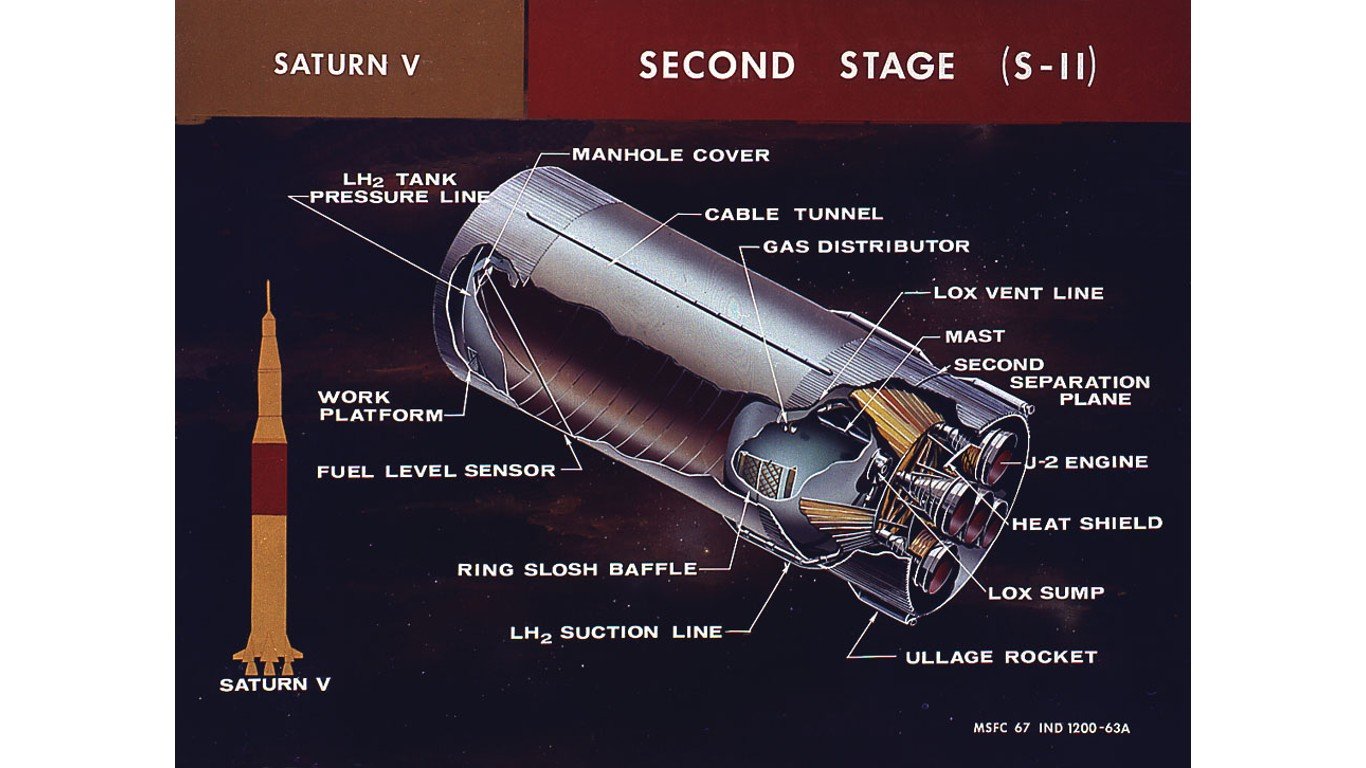
3. Saturn S-II-13 (Skylab rocket)
> Reentry Weight: 45.1 tons
> Re-entry location: Atlantic Ocean (near Madeira)
> Date of crash: January 11, 1975
The massive S-II rocket stage was part of the modified Saturn V rocket that put Skylab, the first U.S. space station, into orbit. After circling the planet for nearly two years, the S-II made an uncontrolled re-entry over the North Atlantic near the Portuguese autonomous region of Madeira, an archipelago about 320 miles west of Morocco.
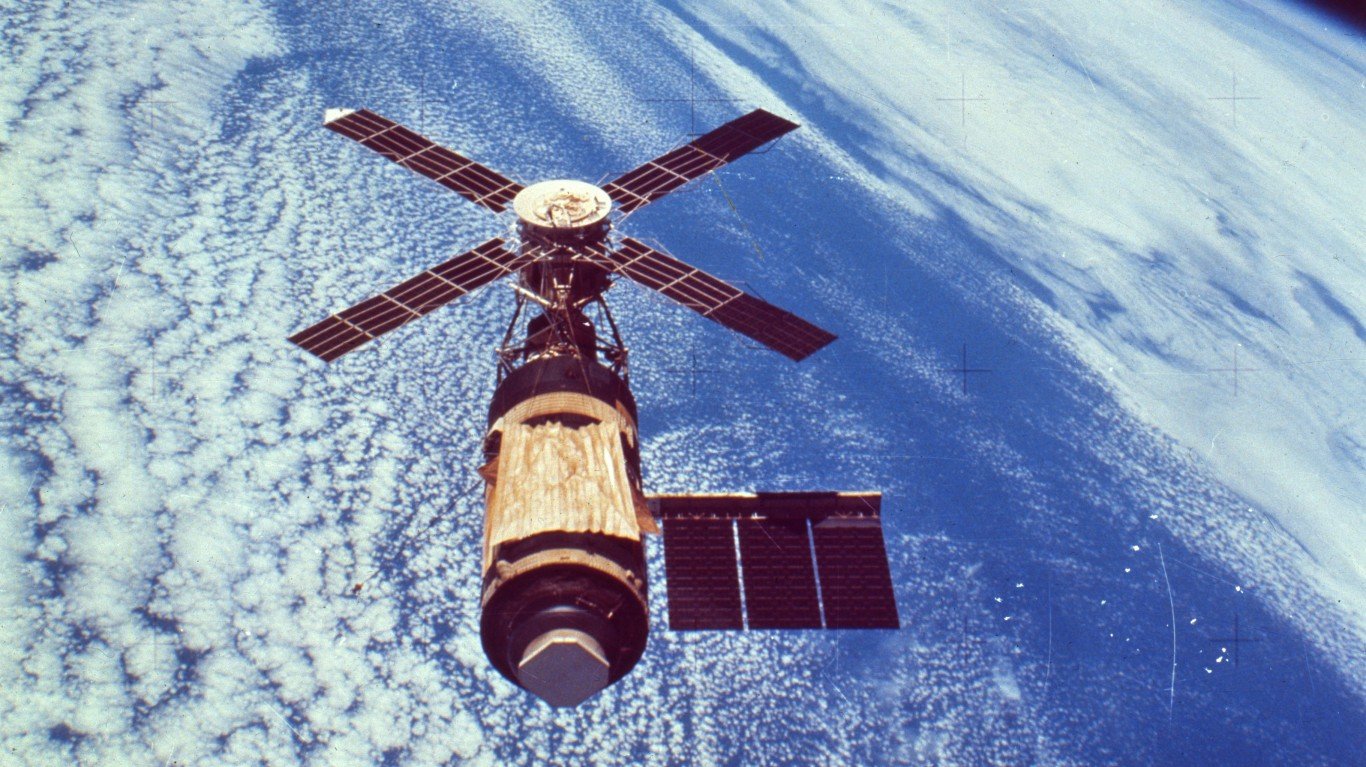

2. Skylab space station
> Reentry Weight: 75.7 tons
> Re-entry location: Western Australia/Indian Ocean
> Date of crash: July 11, 1979
Skylab was the first U.S. space station, designed as a low-orbit scientific research output. Though it was initially designed to last years, the station was crewed for only a few months in 1973 and 1974. By 1978, Skylab’s orbit was decaying, and due to budget constraints NASA had failed to build any control mechanisms for a controlled re-entry. A Hail Mary attempt to force the station to tumble into the Indian Ocean by strategically firing its booster rockets almost worked, but some of the debris landed in western Australia.

1. NASA Space Shuttle Columbia
> Reentry Weight: 106.4 tons
> Re-entry location: USA (Louisiana, Texas)
> Date of crash: February 1, 2003
The Space Shuttle Columbia is the heaviest spacecraft to have plunged back from orbit, also the only one that cost lives. (The NASA Space Shuttle Challenger explosion of 1986 occurred during takeoff.) All seven crew members were killed when Columbia exploded over Louisiana and east Texas. The cause of the disaster was later linked to a piece of foam insulation that had broken off the shuttle’s propellant tank during the shuttle’s descent to Kennedy Space Center. The shuttle was in a controlled descent until it broke apart, but the consequences — raining space debris on land — were similar to uncontrolled crashes.




