Hosting the Olympic Games is a unique honor. Many of the world’s largest cities have lobbied for the right to host the world’s foremost sporting competition — yet only a handful are able to say that they have hosted the Olympics.
To provide a list of the locations of the last 31 Olympic Games, 24/7 Tempo reviewed the dates and locations for the modern Summer Olympic Games listed on The Library of Congress.
The first modern Olympics took place in 1896 in Athens, Greece — the home of the original competition, which dates back centuries. It is one of just 23 different cities to host the Summer Games, most of which are in Europe. Five have taken place in North America, four have been in Asia, two were in Australia, and just one has gone to a South American city.
The COVID-19 pandemic has shaken up the 2020 games. Though it might seem a bit odd to see the Tokyo 2020 logo in the background of an event taking place in 2021, organizers have had to contend with challenging circumstances before. Previous Olympics have been postponed by war or terrorist attacks, and shaken up by international politics.
The Olympics are ultimately about unity, providing a reason for a country to all rally together to support the athletes representing their home nation. In recent Olympic history, a handful of athletes have stood out from the crowd by delivering superlative performances, taking home many gold medals and putting themselves on the pantheon of the greatest athletes ever. These are the 40 most successful athletes of the 21st century.
To determine the locations of the last 31 Olympic Games, 24/7 Tempo reviewed the dates and locations for the modern Olympic Games listed on The Library of Congress. Our list only includes Summer Olympic Games, and also includes the 1916, 1940, and 1944 Olympic Games which were cancelled due to World War I and World War II respectively. The 2020 Olympic Games held in Tokyo, Japan are labeled as 2020 despite delayed competition occurring in 2021 due to the global COVID-19 pandemic.
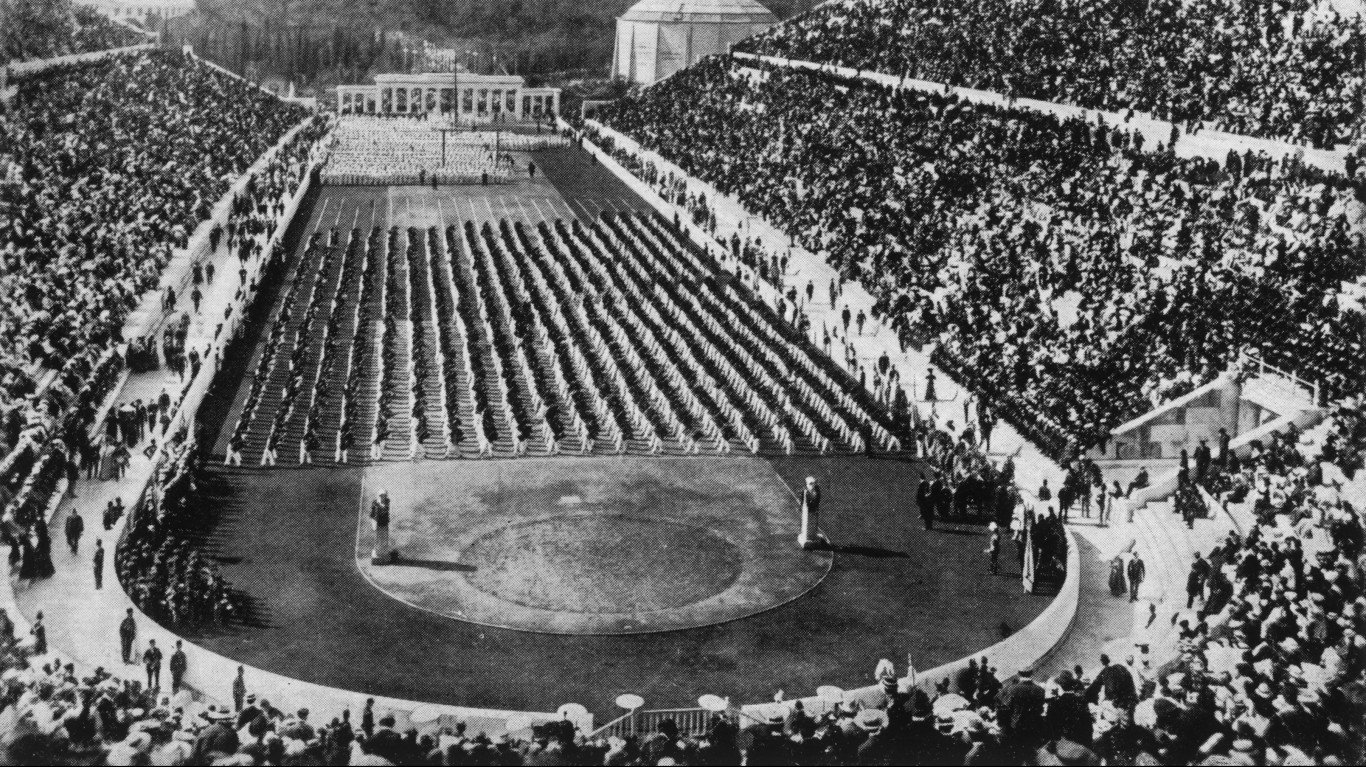
1896 Summer Olympics: Athens, Greece
The first modern Olympics took place in Athens, Greece, in 1896. The Olympiad took place on a much smaller scale than the Games of today — just 12 countries competed. The U.S. team took home the most gold medals, with 11, but Greece won 47 total medals, which was far and away the most of any nation.
1900 Summer Olympics: Paris, France
The 1900 Summer Olympics were set in Paris to coincide with the World’s Fair. France dominated on home soil winning 111 medals, 31 of them gold. The U.S. was second in the medal count at 48. These Games were the first to allow women to compete. Hélène de Pourtalès was a member of the Swiss sailing team that won gold, making her the first ever female Olympic gold medalist. Great Britain’s Charlotte Cooper became the first individual female gold medalist in history, winning the singles tennis event.
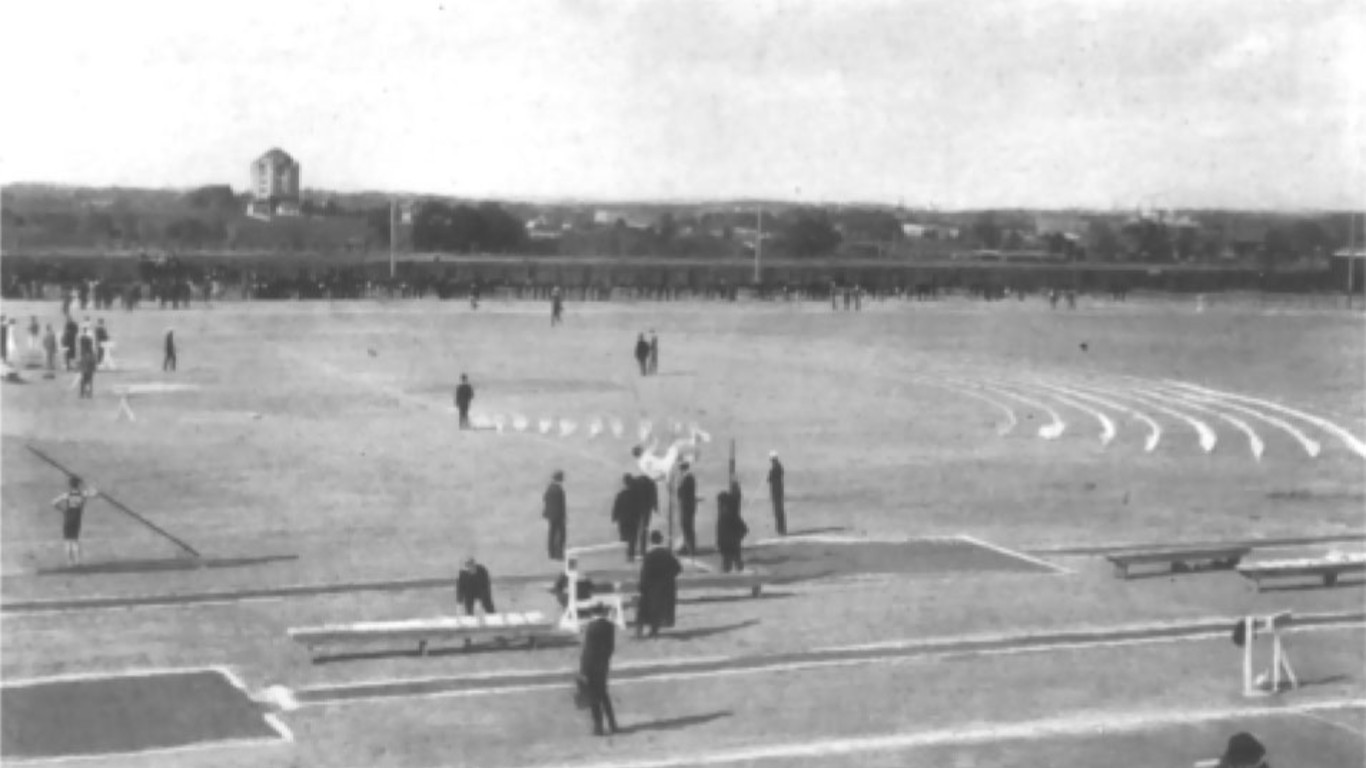

1904 Summer Olympics: St. Louis, Missouri
St. Louis edged out Chicago, New York City, and Philadelphia to hold the first Olympics in America. The Games failed to attract much interest from other countries. Athletes representing the U.S. took home a total of 248 medals. Germany ranked second in the medal count with 14. These Games included events like tug-of-war, golf, and lacrosse.

1908 Summer Olympics: London, England
The 1908 Olympics were initially awarded to Rome, but economic problems and the 1906 eruption of Mt. Vesuvius caused the Italian government to back out of hosting duties. London took up the mantle. The 1908 were the most internationally attended to date, as athletes from 23 nations competed. In addition to Summer Olympics mainstays like swimming, diving, and gymnastics, the 1908 Games featured events such as figure skating, bicycle polo, and motorboating. Great Britain’s athletes took home 146 total medals — 99 more than the second place Team USA.
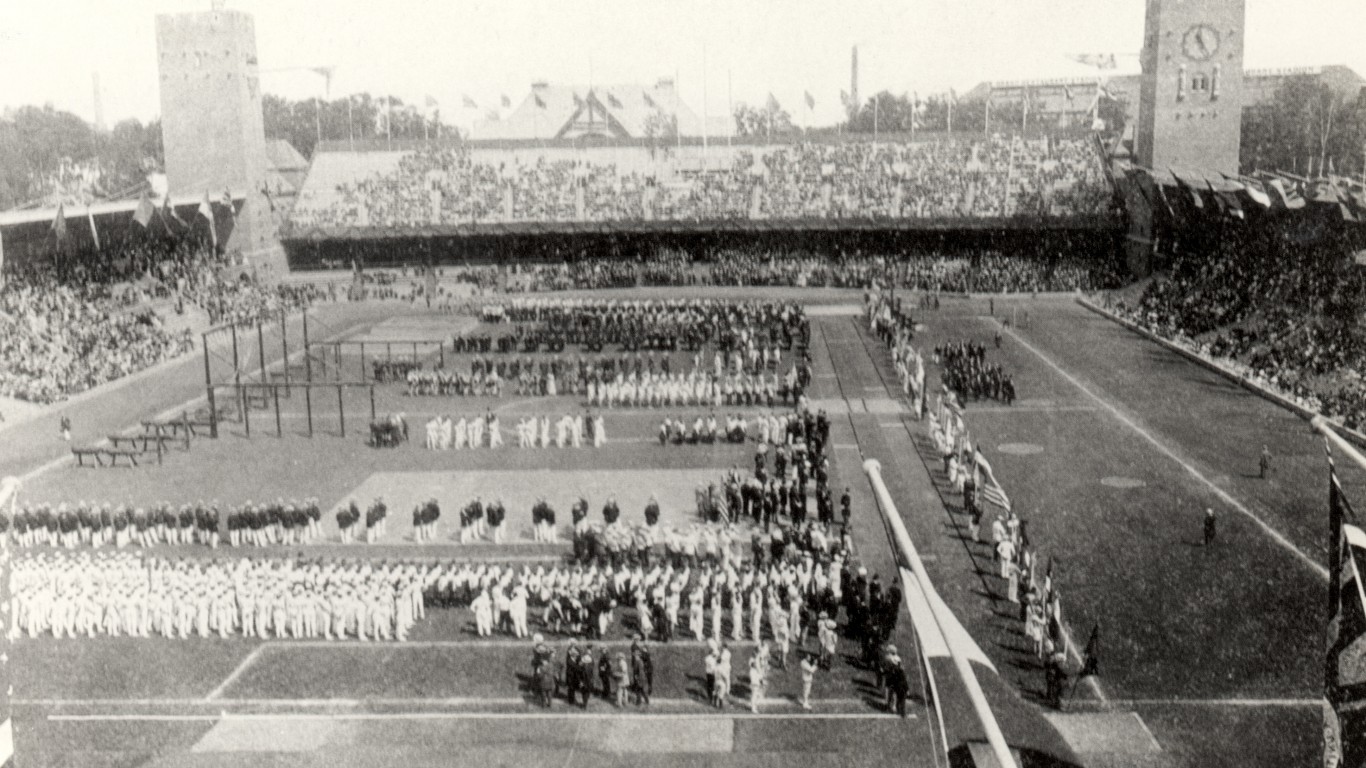

1912 Summer Olympics: Stockholm, Sweden
The 1912 Summer Olympics in Stockholm featured over 2,400 competitors from 29 countries. Swedish competitors took home the most total medals — 65, with 24 golds. But the U.S. athletes won 26 golds out of a total 64 medals. Two of these American golds went to Jim Thorpe, who dominated the Pentathlon and Decathlon. After winning gold in both events, Sweden’s King Gustav V declared Thorpe “the greatest athlete in the world.”

1916 Summer Olympics: Berlin, Germany (Cancelled, WWI)
Berlin was selected to host the 1916 Olympic Games, ahead of Alexandria, Egypt and Budapest, Hungary. Initially, organizers wanted to add winter sports like ice hockey, Nordic skiing, and speed skating into the mix, but the outbreak of World War I in 1914 nixed the Games altogether.

1920 Summer Olympics: Antwerp, Belgium
The 1920 Olympics were the first time in modern history that the host nation did not win the most total medals. Belgian athletes took home 42 medals, tied for fourth with France. The U.S. delegation won 95, Swedish athletes won 64, and British competitors won 43. Germany, Austria, Hungary, and Bulgaria were banned from the Games, as they were deemed aggressor nations in World War I.

1924 Summer Olympics: Paris, France
Paris became the first two-time Olympic host city in modern history in 1924. These Games were more organized and better attended than their initial Olympics in 1900. There were over 3,200 competitors from 45 different nations taking part in 131 different medal events. The 1924 Olympics featured art competitions in the fields of architecture, literature, painting, and sculpture. The U.S. dominated the medal count, taking home 45 golds and 99 medals in total. Host nation France finished second with 41 medals in total.

1928 Summer Olympics: Amsterdam, Netherlands
Amsterdam was selected over Los Angeles as the 1928 Olympics host city. Yet American competitors still dominated the field, taking home 56 medals. Germany, returning to the Games following its World War I banishment, had its athletes win 39 medals. The 1928 Olympics also saw women take another step towards equality, as it was the first time female competitors were able to compete in track & field events — though they only had five events, compared to 21 for male competitors.
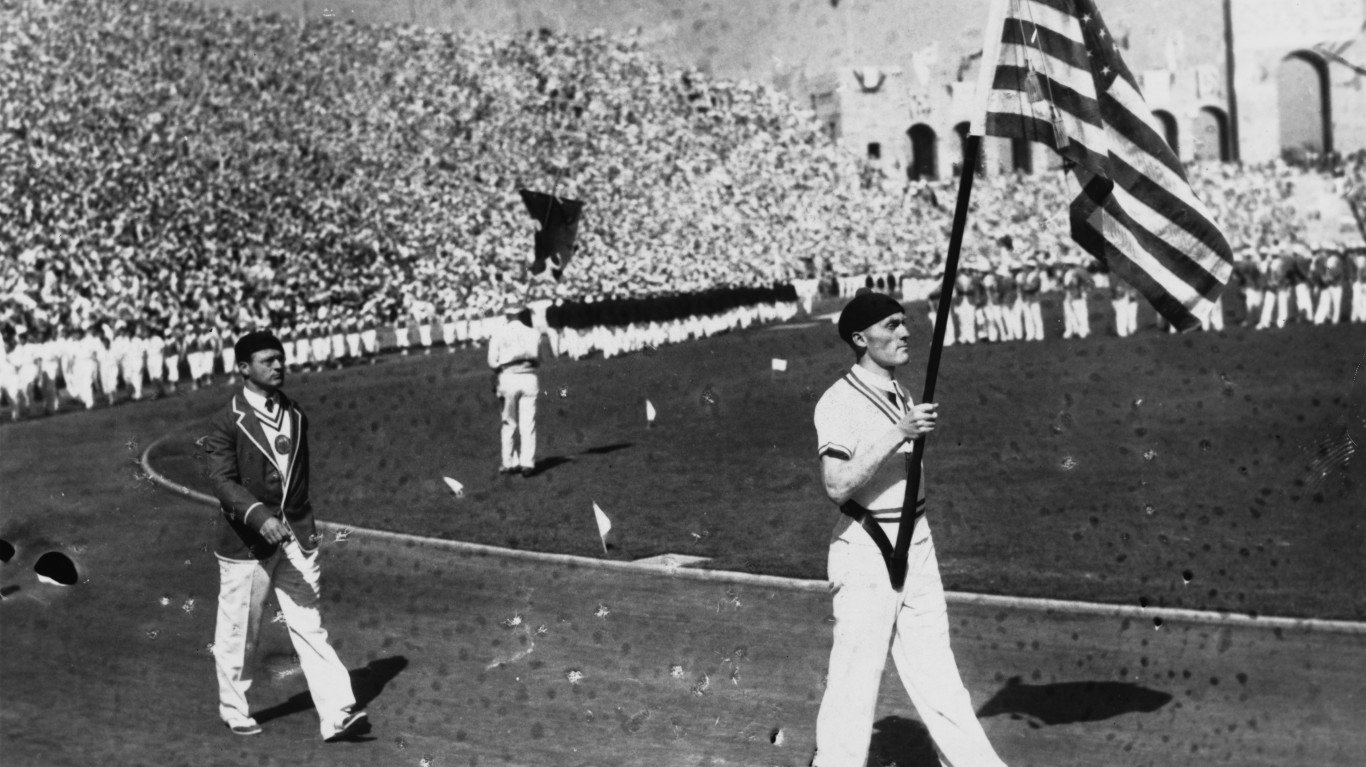

1932 Summer Olympics: Los Angeles, California
The 1932 Olympics were the second held in the U.S. The Great Depression put a damper on the proceedings. The number of participants fell from nearly 3,300 in the previous Games to fewer than 2,000. The U.S. delegation lapped the field, winning 110 medals. Italy finished second with 36. Texan Babe Didrikson was the breakout star of the 1932 Olympics, winning gold in the 80 metres hurdles and javelin and a silver in the high jump. She would later go on to be one of the greatest female golfers of all time.
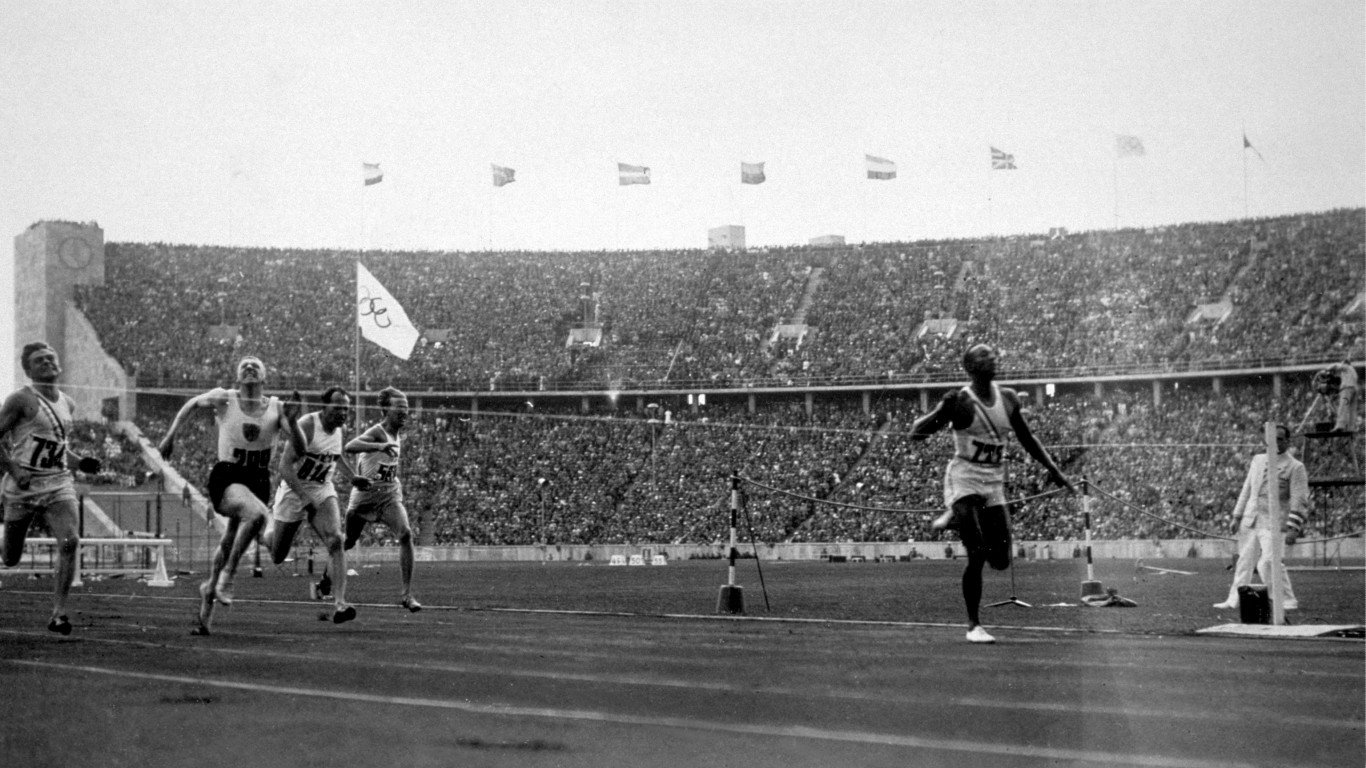
1936 Summer Olympics: Berlin, Germany
The 1936 Olympics in Berlin were marred from the outset, with the U.S., Great Britain, and France nearly boycotting the Games due to the Nazi regime in power at the time. German athletes won 101 medals, by far the most, compared to 57 won by Americans. Yet the enduring image from the 1936 Olympics remains Black American Jesse Owens winning four golds in the 100 metres, 200 metres, 4×100 metre relay, and long jump — denying Adolf Hitler’s ambition to use the Olympics to push the myth of Aryan supremacy.

1940 Summer Olympics: Helsinki, Finland (Cancelled, WWII)
For the second time, a massive worldwide conflict canceled the Olympics. Tokyo was initially supposed to be the first country outside of Europe or the U.S. to host the Olympics, but pulled out in 1938 as it went to war with China the year before. Helsinki and Finland stepped in to host the Games, but the Soviet Union attacked the country in 1939. With war breaking out among many of the world’s countries, the Games were scrapped in 1940.

1944 Summer Olympics: London, England (Cancelled, WWII)
Though there was never a formally published announcement that the 1944 Olympics were canceled, that was the last thing on many people’s minds that year — particularly in London. The Great Britain capital city had won its bid to host the 1944 Games in 1939, but as the German blitz wore on, it became clear the Olympics would not take place.
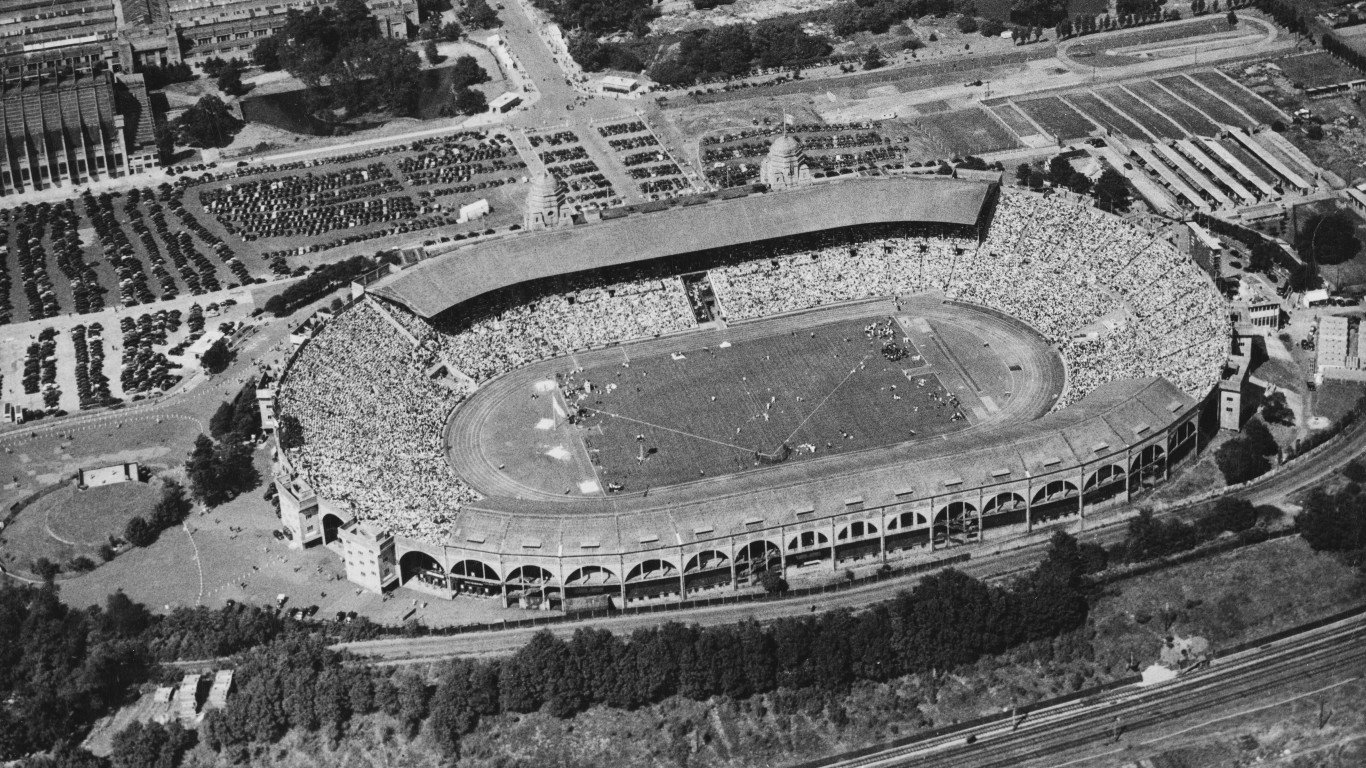

1948 Summer Olympics: London, England
Though London was still recovering from World War II and the blitz in 1948, the games of the XIV Olympiad it hosted was a success. More than 4,400 participants from 59 countries competed — Japan and Germany were barred and the Soviet Union opted not to compete. U.S. athletes remained the most successful contingent, taking 84 medals, including 38 golds. Great Britain won 27 medals.
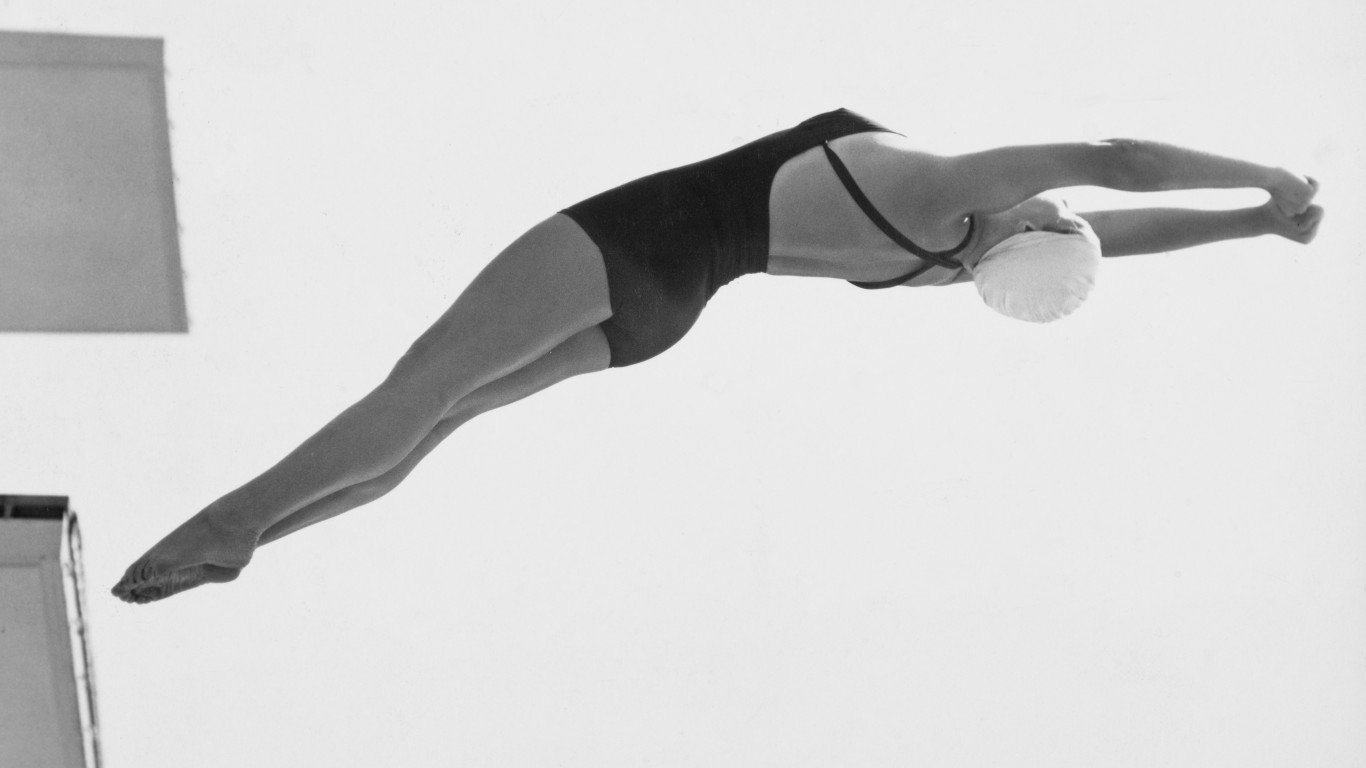

1952 Summer Olympics: Helsinki, Finland
Like London four years prior, Helsinki was finally able to host the Olympics it had been denied by World War II in 1952. Though the U.S. topped the medal count again, with 76, it would be the Games in which the Soviet Union established itself as a serious contender. The nation finished second with 71 total medals. Soviet gymnast Viktor Chukarin won six medals in the 1952 Games — gold in the individual all-around, team all-around, horse vault, and pommelled horse, and silver in the parallel bars and rings.

1956 Summer Olympics: Melbourne, Australia
When Melbourne, Australia won its bid for the 1956 Summer Olympics, it marked the first time a country outside of Europe or North America hosted the Games. The Soviet Union won the most gold, silver, and bronze medals, taking home 98 in total. The U.S. finished second with 74. This 16th Olympiad was also the first one to feature a closing ceremony, with all competitors marching in as a group to symbolize how athletes from around the world had come together during the Games.
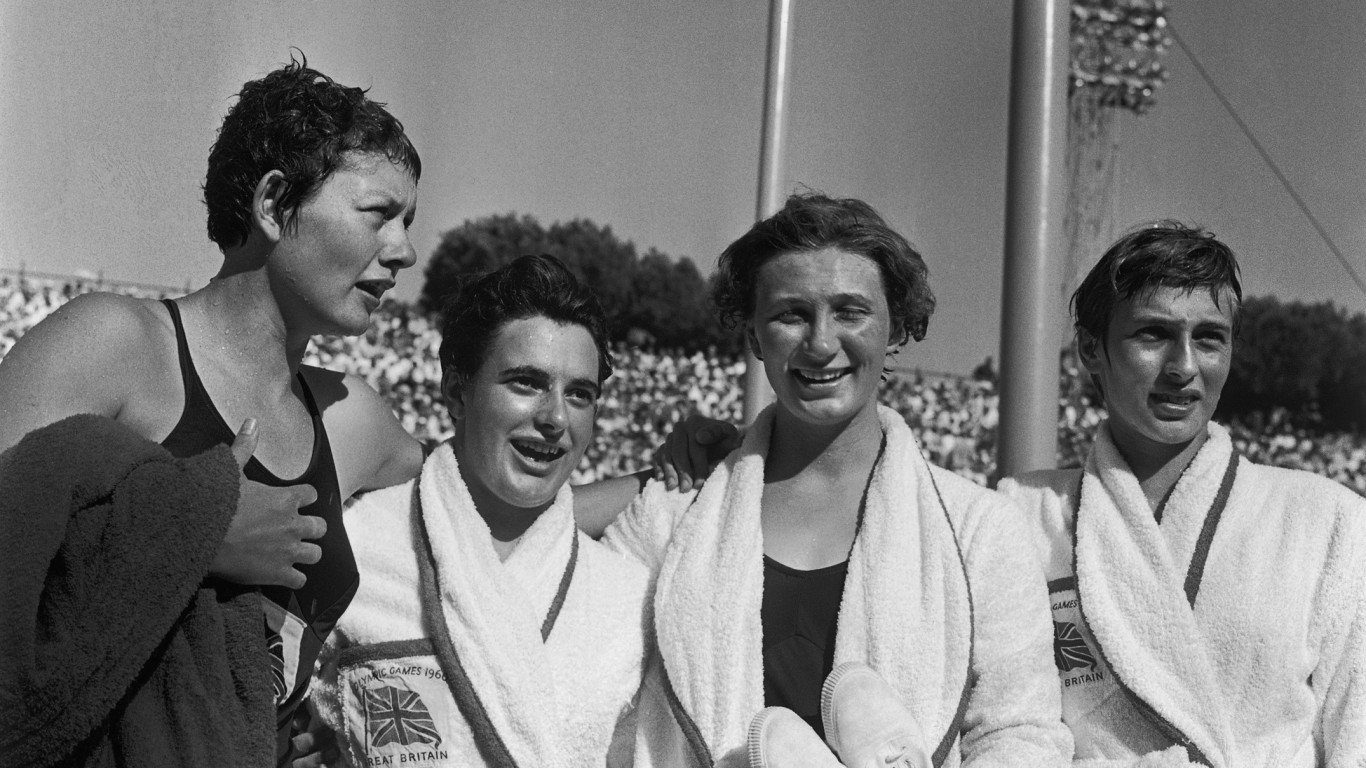

1960 Summer Olympics: Rome, Italy
The 1960 Rome Olympics were the biggest in history, with 5,350 competitors from 83 countries. Notable names like Cassius Clay, Oscar Robertson, and Jerry West competed for the U.S., but it was again the Soviet Union that came away with the most medals — 103 to the U.S.’s 71. Abebe Bikila of Ethiopia became the first Black African to win an Olympic gold medal when he pulled away from Morocco’s Rhadi Ben Abdesselam to win the marathon.
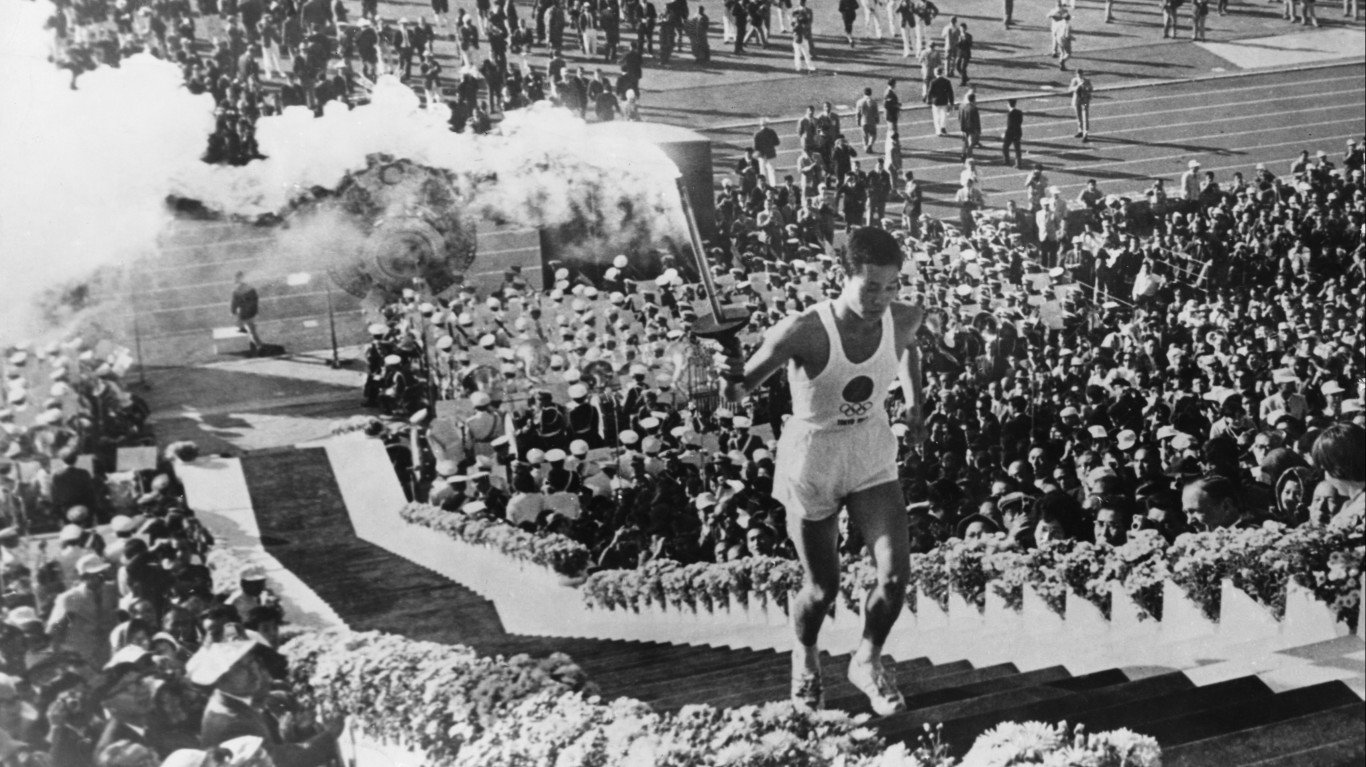

1964 Summer Olympics: Tokyo, Japan
The 1964 Summer Olympics in Tokyo were the first held in Asia. Though the Soviet Union won more total medals, 96, than the U.S. did, 90, American competitors had the edge in gold medals 36-30. Four of those golds went to Yale’s Don Schollander, who became the first swimmer to take home four golds in one Games — finishing first in the 100 and 400 meter freestyle, as well as the 4 x 100 and 4 x 200 relays.

1968 Summer Olympics: Mexico City, Mexico
In the 1968 Summer Olympics in Mexico City, the U.S. returned to the top of the international sporting world, with its representatives taking home 107 medals, beating out the Soviet Union with 91.
The enduring image from the 1968 Mexico City Olympics is Tommie Smith and John Carlos raising their fists in a Black power salute as they stood on the podium following their race. The paid agreed to use their platform to advocate for equality. The symbol came just months after Martin Luther King Jr. was assassinated, and led to a cascade of backlash not only for them, but for Australia’s Peter Norman who was on the podium with them.
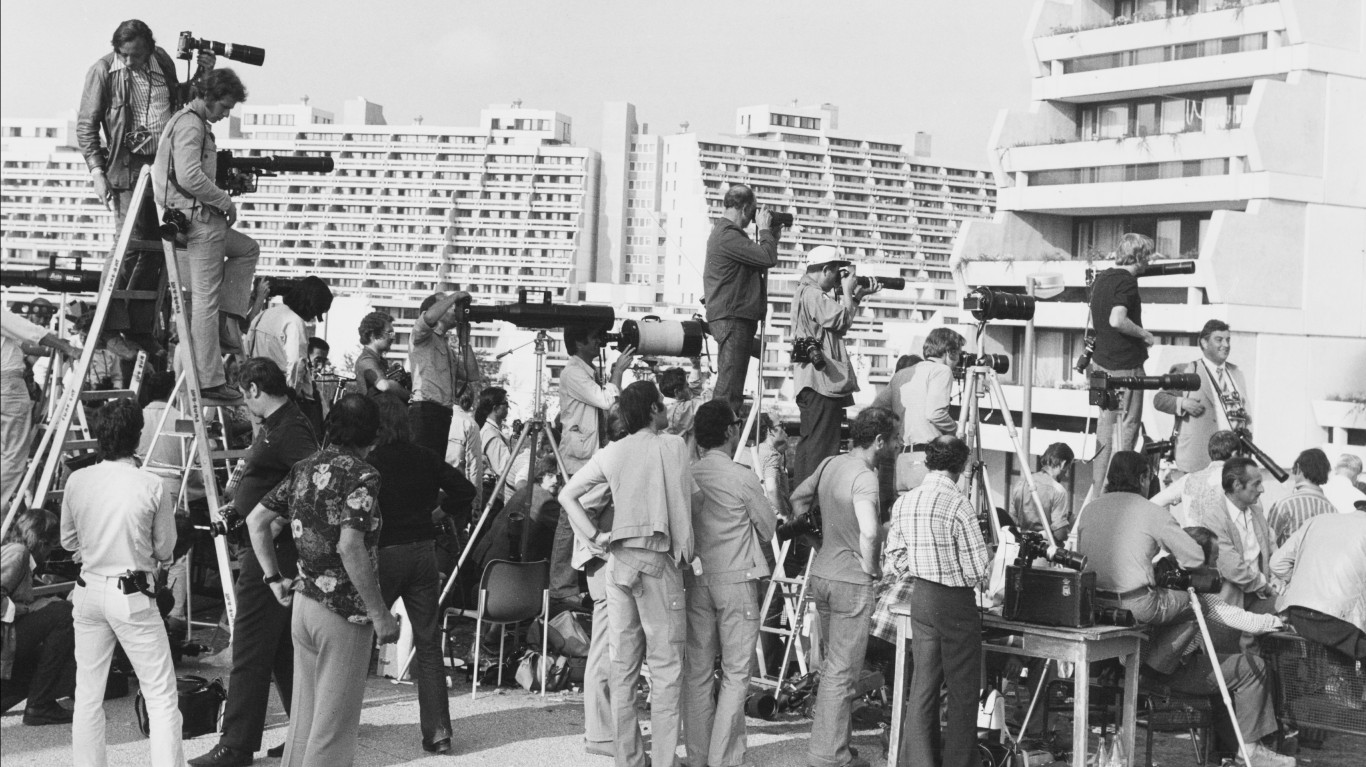

1972 Summer Olympics: Munich, Germany
The 1972 Munich Games are perhaps best remembered for the terrorist attack that took place. Palestinian terrorists broke into the Israeli athlete’s compound in the Olympic Village, killing two and taking nine hostages, demanding that Israel release 230 Arab prisoners. After a shootout with authorities in the Munich airport, all nine Israeli hostages were killed, along with five kidnappers and one policeman. The Games were postponed for 24 hours.
As for the Games themselves, the Soviet Union won 99 medals, 50 of which were gold. The U.S. won 94 medals. East Germany took home the third-most medals, with 66, followed by West Germany with 40.
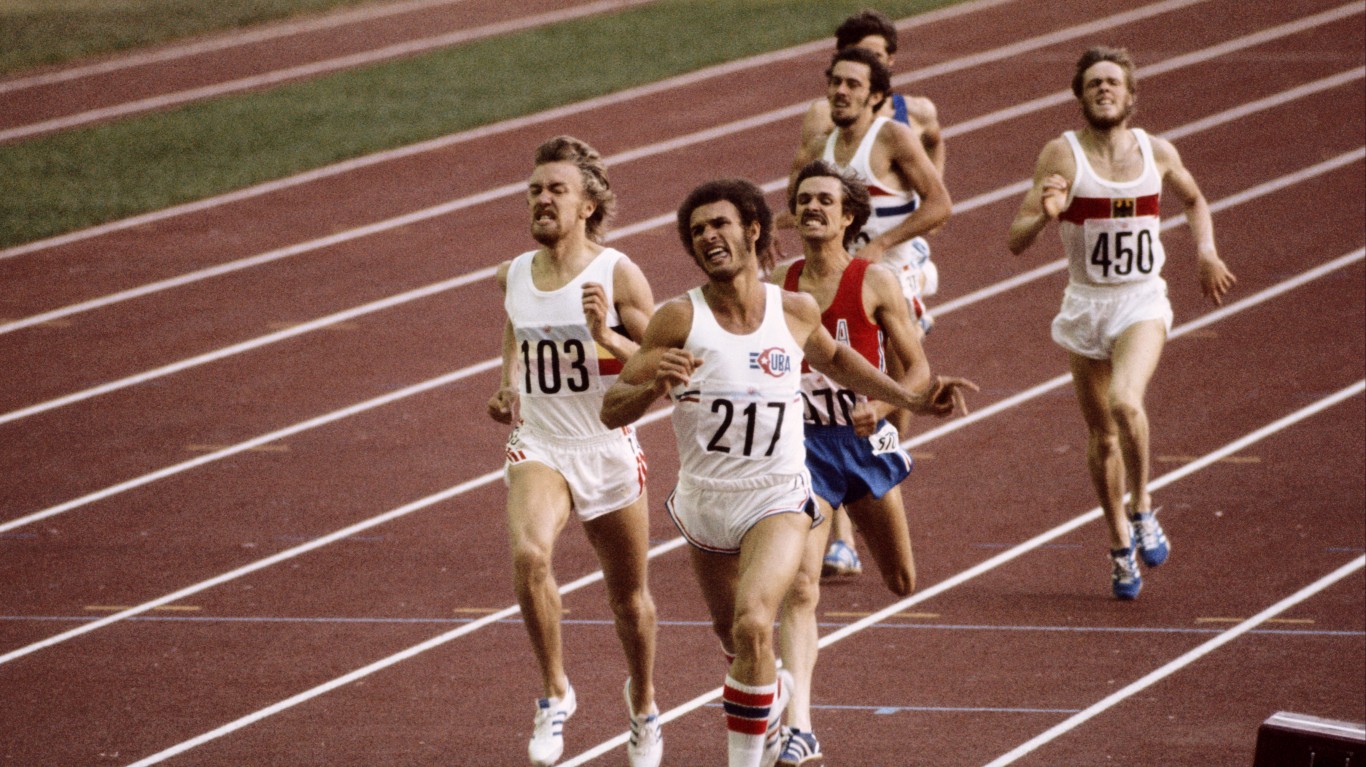

1976 Summer Olympics: Montreal, Canada
More than 40 years later, the 1976 Olympics in Montreal are now remembered not for the Games themselves, but the lingering financial crunch it left with the home city. The cost of putting on the Games ballooned to 13 times the original estimate and left the city over $1 billion in debt, which was not paid off for 40 years.
The star of the 1976 Olympics was Soviet gymnast Nikolay Andrianov. He won seven medals — gold in the individual all-around, floor exercise, horse vault, and rings, silver in the team all-around and parallel bars, and bronze in the pommelled horse. His performance helped the Soviet Union dominate the field, winning 125 medals. The U.S. was second with 94.
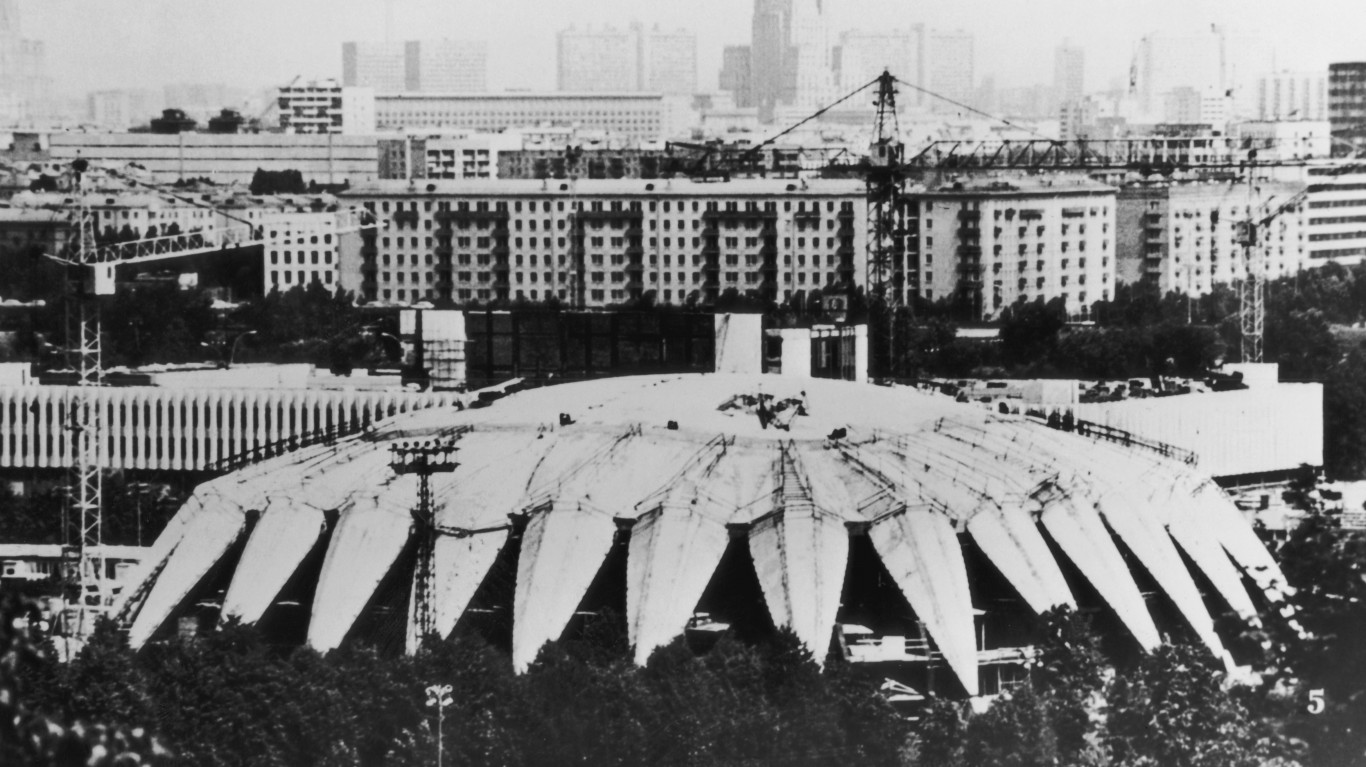

1980 Summer Olympics: Moscow, Soviet Union
The 1980 Summer Olympics in Moscow was broadly boycotted in response to the Soviet Union’s invasion of Afghanistan. Dozens of countries opted to skip the Games, including the U.S., Canada, Japan, China, and more. With powerhouse countries like these dropping out, it left the Soviets to dominate the field. Its athletes won 195 medals. East Germany finished second, winning 126.
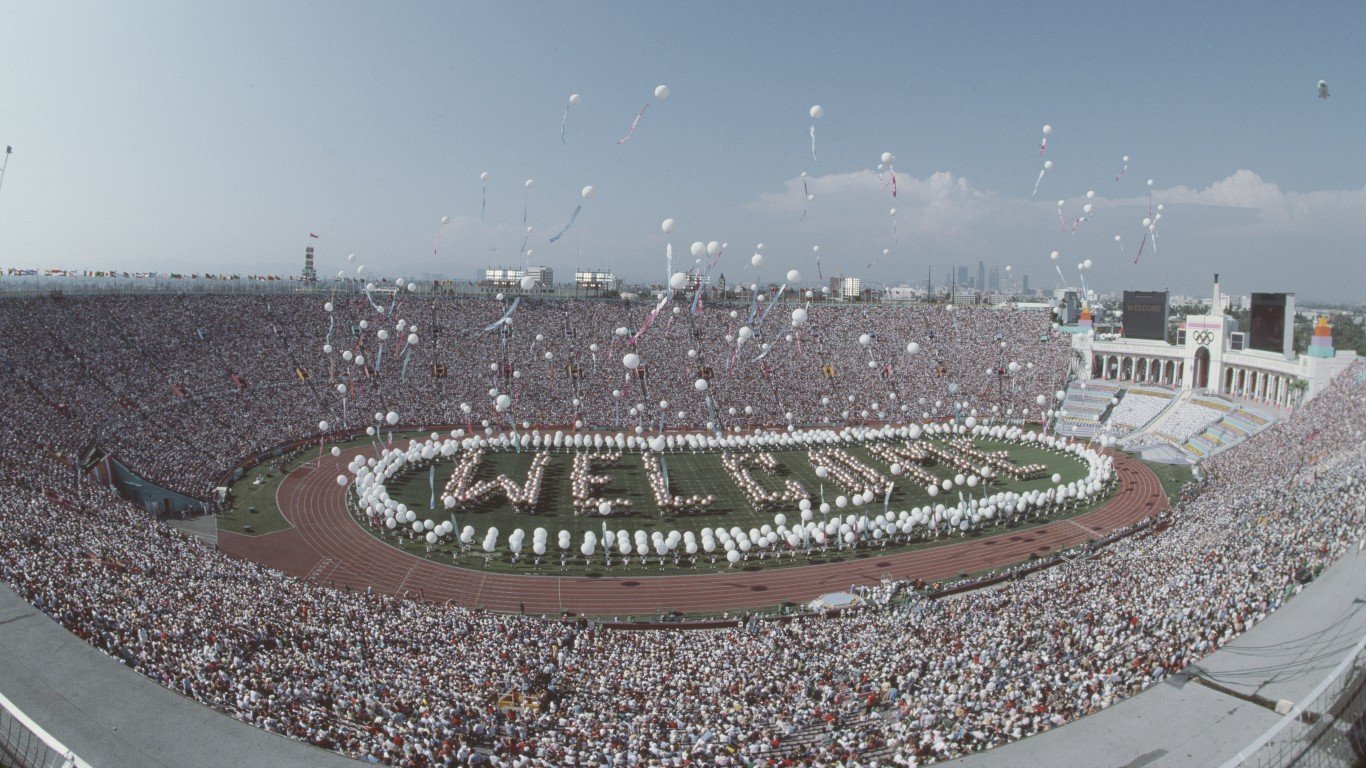
1984 Summer Olympics: Los Angeles, California
After skipping the 1980 Games, the U.S. hosted the Olympics in 1984 — only for the Soviet Union and several other Eastern European nations to drop out, citing “anti-Soviet and anti-Communist activities” in the area. With major competitors out, the U.S. athletes crushed all comers, winning 174 medals. The next closest country was West Germany with 59. The Los Angeles Games were also notable because they turned a $200 million profit — a feat other Olympics have struggled to replicate.
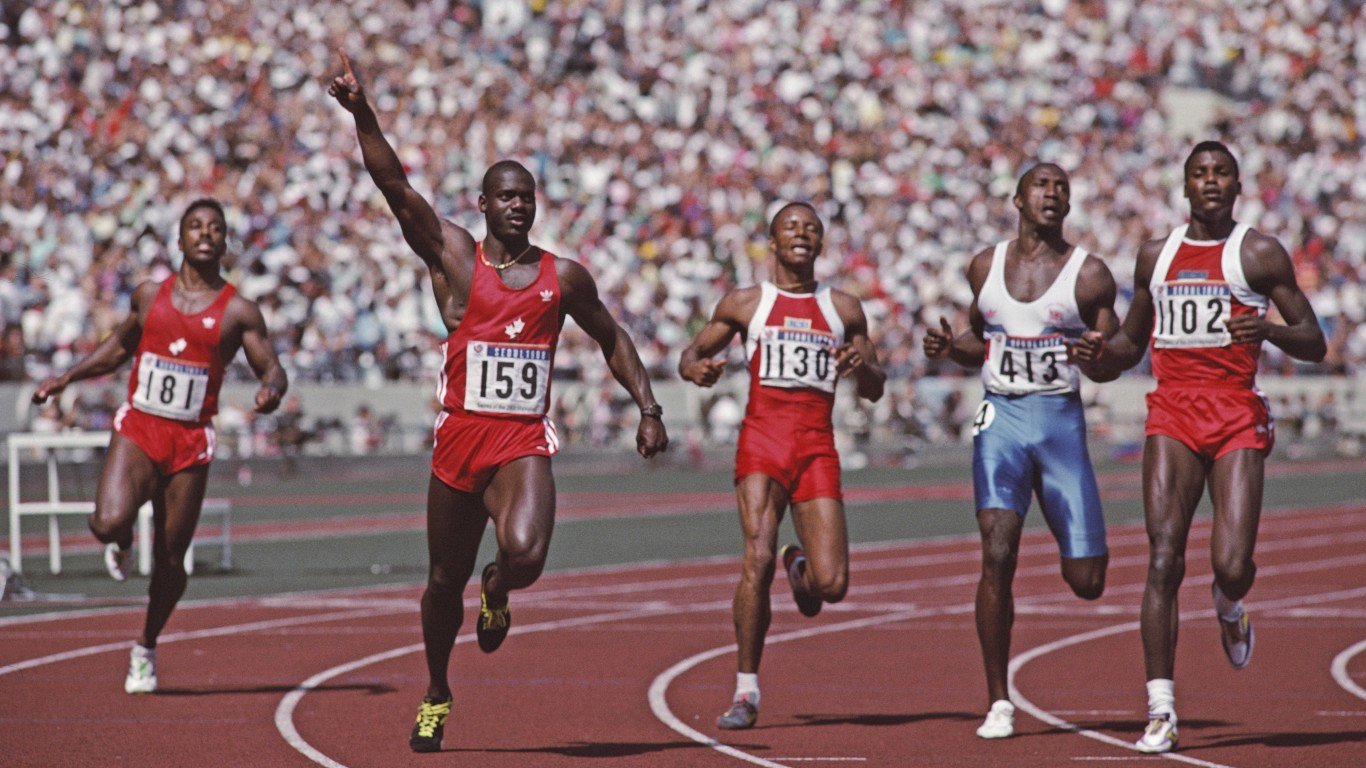

1988 Summer Olympics: Seoul, Republic of Korea
The International Olympic Committee risked a third heavily-boycotted Olympics in a row when they awarded the 1988 Games to Seoul — several countries did not have diplomatic relations with South Korea, as they were aligned with North Korea. Though Cuba and Ethiopia boycotted, the Soviet Union and other nearby nations competed anyway. This proved to be a wise decision, as the Soviet Union and East Germany both took home over 100 medals, while the U.S. medal tally was third, with 94. East German swimmer Kristin Otto took gold in all six of her events.

1992 Summer Olympics: Barcelona, Spain
The 1992 Summer Olympics in Barcelona broke the record for the most countries and competitors in one single Olympics. Over 9,300 competitors from 169 countries flocked to Spain to compete. The world was in flux as the Games began — the Soviet Union had just broken up, Germany reunified, and Yugoslavia became several independent countries. Athletes from these areas competed as a “Unified Team” and won 112 medals, narrowly edging out the U.S. with 108. Germany was third with 82.
These Olympics are likely best remembered for the “Dream Team” when the best basketball players in the world played for Team USA and routed the competition en route to the gold.

1996 Summer Olympics: Atlanta, Georgia
On home soil, American athletes dominated the 1996 Atlanta Olympics. U.S. competitors won 101 medals, including 44 golds. The relatively newly-formed nations of Germany and the Russian Federation finished second and third, respectively.
Like several before, these Games were interrupted by violence. Far-right extremist Eric Rudolph set off three bombs that killed two and injured over 100 in Centennial Olympic Park. Rudolph said he wanted to embarrass the U.S. for legalizing abortion. He was eventually captured in 2003.

2000 Summer Olympics: Sydney, Australia
The 2000 Summer Olympics in Sydney were a welcome change from the violence and political turmoil that had rocked the previous contests of recent years. The 2000 Olympics marked the debut of a handful of competitions, including trampolining and taekwondo. Ultimately, the U.S. competitors took home the most medals, 93, edging out Russia’s 89.

2004 Summer Olympics: Athens, Greece
In 2004, the Olympics returned to their ancestral homeland of Greece. Over 10,000 athletes from 201 countries came to Athens to compete. In a nod to history, shot putters competed in the Ancient Olympic Stadium and marathon runners ran the original marathon course — beginning in the village of marathon and running to the Panathenaic Stadium. America topped the medal standings, with 101 medals and 36 golds.

2008 Summer Olympics: Beijing, China
The 2008 Summer Olympics in Beijing were spectacular from start to finish. The Opening Ceremony is still remembered fondly as perhaps the best ever. The unquestioned superstar of the 2008 Games was American swimmer Michael Phelps. He won all eight events on his docket, becoming the first athlete to win eight golds in one Games, as well as the first to hold 14 total golds. Jamaica’s Usain Bolt also made a splash, winning the 100 meter dash in style and setting a world record of 9.69 seconds in the process.

2012 Summer Olympics: London, Great Britain
London became the first three-time Olympics host in modern history when it held the 2012 Olympic Games. British distance runner Mo Farah became a national hero, winning gold in the 5,000 and 10,000 meter races on home soil. But it was the U.S. that tallied the most medals, at 104. China finished second with 91, and the host nation won the fourth-most total medals, but the third-most golds, at 29.
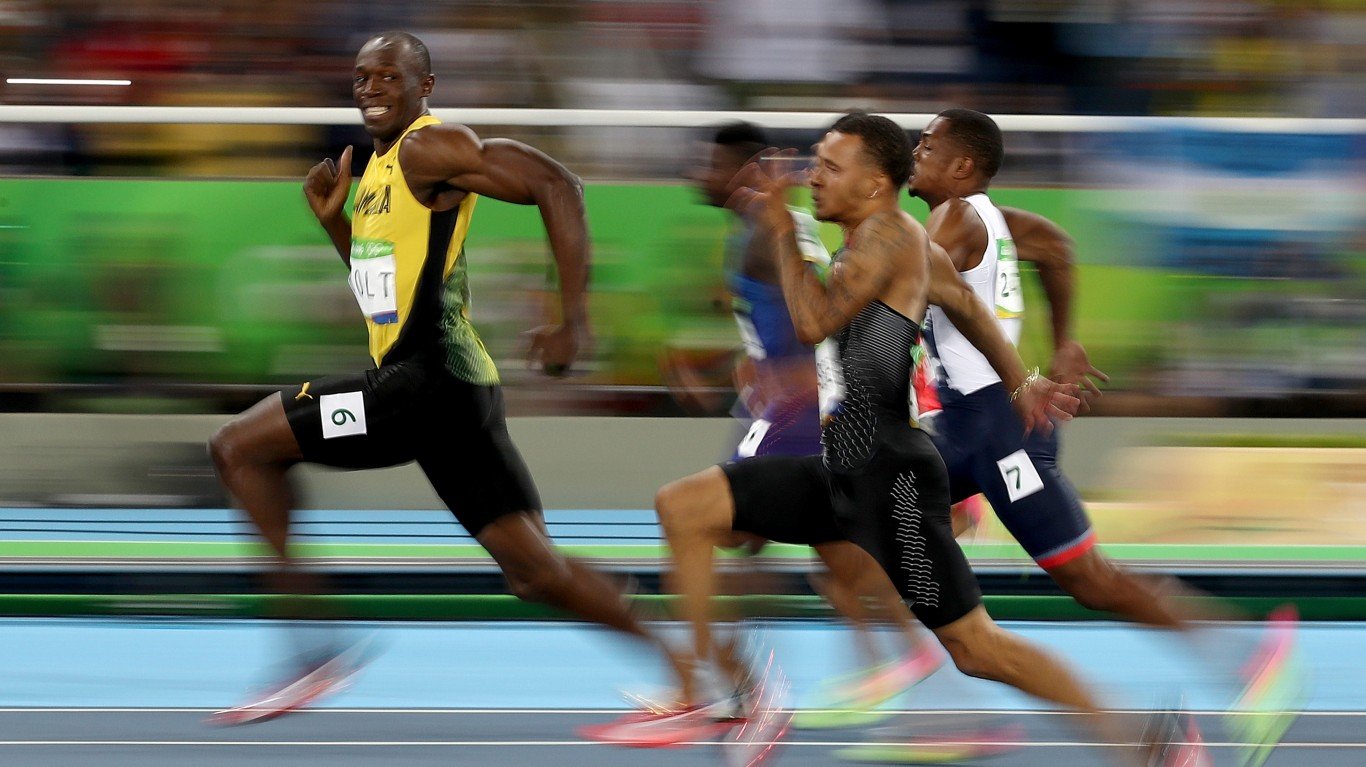

2016 Summer Olympics: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Rio de Janeiro became the first South American nation to host the Olympics when the IOC awarded the Games to the city for 2016. Yet the decision proved to be short-sighted, as the city and Brazil as a whole did not have infrastructure like venues and transportation already in place. All told, the Games cost Brazil over $20 billion — and the tally is increasing, as the cost of maintaining the stadiums is steep. Still, Brazilian fans were thrilled when their soccer team was able to deliver their first gold medal in their most beloved sport. The U.S. again dominated the medal tally, with 121 — over 50 more than the next closest country, which was China. American gymnast Simone Biles emerged as the star of the Games, taking home four golds and a bronze.

2020 Summer Olympics: Tokyo, Japan
The 2020 Summer Olympics are taking place in 2021, as a result of the global COVID-19 global pandemic that pushed the Games back by about a year. Still, nearly 13,000 athletes from 208 countries came to Tokyo to compete. Tokyo beat out Istanbul and Madrid for hosting duties.

